By Merima Crnica and Matthias Kolck
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) not only specifies far more content for sustainability reporting. Above all, it is also a guidepost for the transformation of business models towards sustainability and sometimes intervenes deeply in the organizational structure. It therefore automatically places demands on the governance structures of the companies concerned and also on the management of ESG processes and KPIs.
Many companies that are obliged to report in accordance with CSRD are currently facing the challenge of taking into account their existing management systems, above all their environmental management system in accordance with ISO 14001 or EMAS, to meet the CSRD requirements. Last but not least, the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), as an integral part of the CSRD, mandate the implementation of a procedural integration. We show you how you can derive added value from your CSRD compliance process and expand existing management systems efficiently and sensibly within the framework of the new sustainability reporting obligations.
Background information: Why CSRD and EMS?
To take advantage of the synergies between your environmental management system (EMS) and CSRD, it is important to first understand the purpose of each. An environmental management system in accordance with ISO 14001 or EMAS helps an organization improve its environmental performance and reduce negative impacts. It creates a basis for setting environmental targets and also for fulfilling legal requirements in the environmental field through appropriate measures.
Excursus: European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS)
The ESRS standards are EU reporting standards for sustainability-related information and take sustainability reporting to a new level. Find out more about the ESRS
The CSRD is an EU directive and serves the transparency, transformation and comparability of companies and their sustainability performance. It also sets a new benchmark for sustainability reporting. The topics that a company must address in detail are the result of the double materiality assessment. This is a mandatory tool for CSRD implementation in order to define the individual focus topics of a company.
Overlaps: EMS according to ISO 14001 and EMAS and CSRD criteria
In many parts, the CSRD overlaps with the requirements of ISO 14001 for environmental management systems. This can be seen, for example, by comparing the new reporting structure according to ESRS 2 (using the example of ESRS E1 Climate Change) and the requirements of ISO 14001.
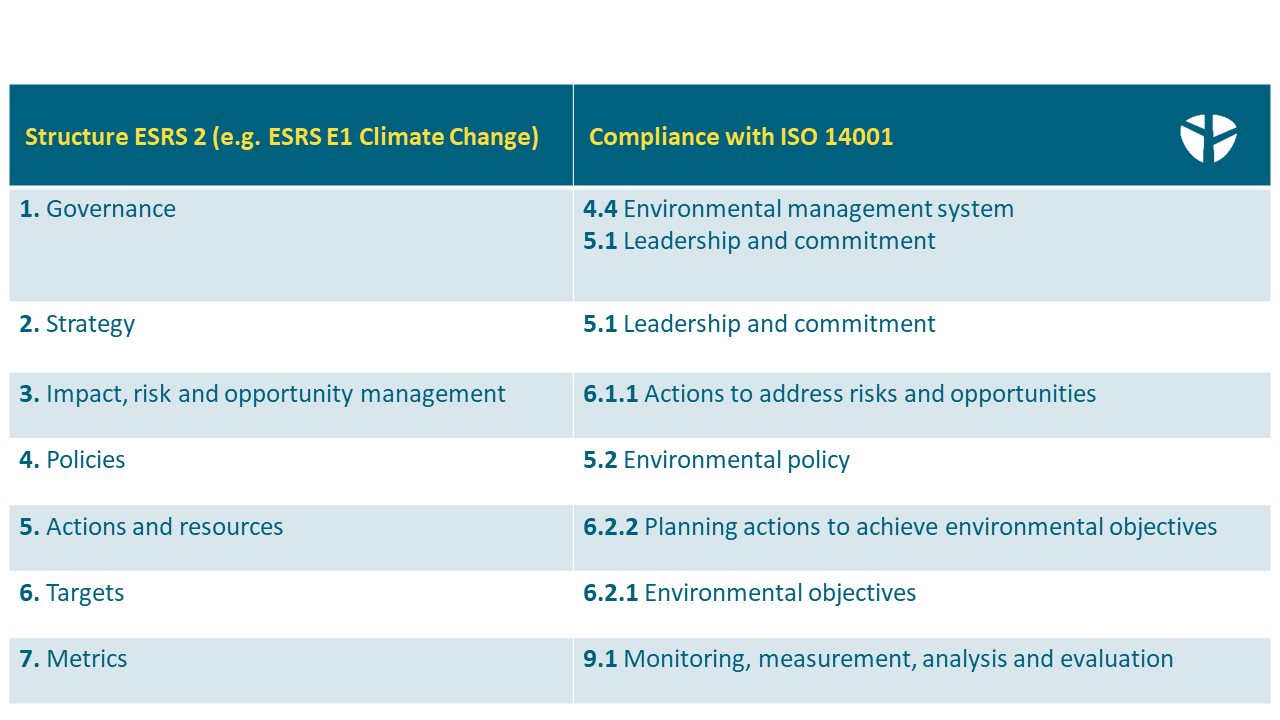
The overlaps show that an environmental management system in accordance with ISO 14001 or EMAS offers the ideal prerequisite for meeting the ESG requirements of the CSRD. After all, you cover a significant part of the CSRD with your environmental management system and thus avoid setting up inefficient parallel systems. For example, some environmental ESRS data points are often already covered by an existing EMS in accordance with ISO 14001. Usually, a portfolio of measures has also been developed as part of your EMS, which can be incorporated into your roadmap for CSRD implementation. Existing governance structures also provide a suitable starting point for working on your CSRD governance.
3 steps: How to use your EMS for CSRD implementation
Internal Engagement
Environmental management is not always located in the same department as sustainability management . If this is the case, the first important step is to initiate cross-departmental cooperation.
Gap analysis
The responsible persons must then ask themselves which CSRD requirements apply to the company. The joint gap analysis shows which aspects are already fulfilled by the existing environmental management system and where there are gaps.
Roadmap
To close the gaps, a roadmap with suitable measures and milestones is derived. This will systematically expand the existing control structures of your environmental management system on the way to CSRD compliance.
5 benefits of aligning your EMS with your CSRD obligations
Merging your EMS and your CSRD roadmap leads to numerous synergies and benefits:
1
2
3
Aligning sustainability, environmental and energy management means that the overall portfolio of requirements can be met efficiently.
Environmental management is gradually developing into an instrument for your CSRD compliance. Requirements from the new reporting obligation can be anchored in processes accordingly.
Uniform governance structures and joint documentation facilitate management.
4
5
Tools and methods for both topics can be coordinated and used in conjunction with each other, for example: CSRD materiality assessment and EMS context analysis.
Standardizing your data collection and reporting structures for both requirement areas reduces complexity and ensures efficiency.
Conclusion CSRD and EMS: What we advise to companies
If you already have an environmental management system
Use your existing management systems, structures and processes to successfully implement the CSRD and manage it procedurally. These form a solid basis for dealing with the ESRS. Even before the double materiality assessment is carried out, environmental management, for example, should be involved and take part in workshops.
If you do not yet have an environmental management system
We advise companies that do not yet have an environmental management system to set up an EMS as part of CSRD implementation. This is because certification of your environmental management system in accordance with ISO 14001 or an EMAS environmental statement can be achieved with little additional effort. This will not only score you points in terms of sustainability reporting but also in supplier evaluations. Companies also want to be able to present an improvement in their environmental performance in their management reports. In practice, this improvement is best achieved by implementing an EMS.




